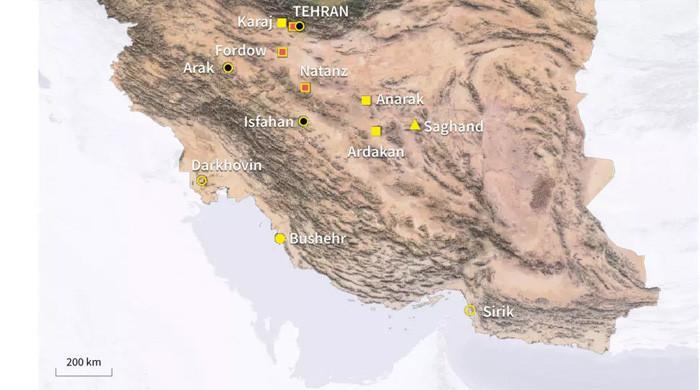
Infographic with a map of Iran showing nuclear sites, reactors and uranium mines. — AFP
#Key #locations #Irans #nuclear #programme #explained
Before the Israeli invasion of Israel on Friday, Washington and Tehran had carried out several rounds of Iran’s nuclear program, as their concerns over rapid expansion had increased.
In recent years, Iran has significantly promoted its nuclear program, after which when the United States unilaterally withdraws, in 2018, a major agreement has been reached globally after the global powers stopped its nuclear activities in exchange for approval from approval.
According to the latest report by the International Atom Energy Agency (IAEA), by mid-May, by mid-May, Iran’s total enriched uranium reservoir is estimated to be more than 45 times in the contract of 9,247.6kg or 2015.
In its reservoir, Iran’s estimate is 408.6kg, up 60 % enrichment – is only a short step from 90 % required for nuclear warheads.
According to the definition of the IAEA based in Vienna, there is now theoretically theoretically for nearly 10 nuclear bombs, nearly nearly grade material, if it has been further improved.
But Iran has always denied the ambitions of the preparation of nuclear weapons.
The following is a list of Iran’s key nuclear sites, which are subject to regular inspection through UN nuclear care.
Uranium enrichment plants
Nuts
About 250 250 km (150 miles) south of Tehran, Nuttans is a major uranium enrichment site in Iran, which was first revealed in 2002.
The nutrients operate about 70 70 wrinkles in their two enrichment plants, one of which is underground. There is a series of streams of centered centers – machines used in the process of enriching uranium.
In April 2021, the site was damaged in an attack that Iran said was a process of sabotage by Israel.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said that on Friday, Israel’s operation attacked the “Iran’s nuclear enrichment program”, targeting nuclear facilities among Nutrients and nuclear scientists.
IAEA chief Rafael Grossi confirmed that the Natis site is “in goals”.
Forto
Under a mountain near the Holy Central Central Nation, the UN was secretly built in violation of UN resolutions, Fordo was first disclosed publicly in 2009.
Initially described as an “emergency” facility that was built underground to protect it from potential air strikes, later Iran indicated that it was a enrichment plan that was capable of accommodating about 3,000 centers.
In 2023, up to 83.7 percent of enriched uranium particles were discovered at the Fordo Plant, which Iran claimed was the product of “non -intended fluctuations” during the enrichment process.
Uranium conversion and research reactor
Asfahn
Uranium conversion in Central Iran’s Isfahan, raw mining uranium is processed in uranium tetrafluoride (UF4) and then uranium hexaflooride (UF6), a feed gas for Sentry Fujis.
The plant was tested in 2004 after its completion.
The Asfahan Center has also supported the convenience of nuclear fuel fabric, which was inaugurated in 2009 and produces less enriched fuel for use in power plants.
In July 2022, Iran announced plans to build a new research reactor there.
Ginger
Work on the Arakari Heavy Water Research Reactor began in the 2000s on the outskirts of Bloodab village, but was stopped under the terms of the 2015 contract.
Meanwhile, Iran has informed IAEA about its plans to commission the reactor by 2026.
The research reactor had to officially prepare a plutonium for medical research and the site also includes a production plant for heavy water.
Tehran
There is a reactor at the Tehran Nuclear Research Center provided by the United States to manufacture medical radiosocopy in 1967.
Nuclear power plant
Look
Russia was built by Russia’s only nuclear power plant in the southern port city of Bushehr, and in 2012, he began working less capacity in 2011 before plugging the National Power Grid.
Russia is continuing to provide nuclear fuel for the plant, which is controlled by IAEA.
In the context of the Islamic Revolution of 1979, a German company started construction at the plant with a thousand megawatts of renovated talent until the project was stopped. Moscow later completed it.
Darcouvin and Serk
Iran started construction at 300 MW power plant in Darcovin, in the southwest of the country in late 2022. In the early 2024, he also started working in the hormows, in the stream of Harmos, at a new complex of four individual plants, which has a joint capacity of 5,000 MW.



